
In recent decades, more and more families need WiFi at home and they originally ask ISP (Internet service provider) to install family Internet. If it’s the first time for us to install the family Internet, we will find the ISP would give us a combined modem, which can provide the function of WiFi.
Now, here is the question.
Should we buy a wireless router separately, if the ISP provided us a WiFi modem?
Let’s discuss.
First, we need to compare a router with a modem.
What Is a Router?
A router is a networking device that forwards data packets between computer networks.
Router is connected to the network in the LAN or WAN equipment. It will automatically select and set the route according to the channel to the best path, in order to send the signal. The wireless router is a router which can provide you WiFi signal.
A modem (modulator-demodulator) is a network hardware device that modulates one or more carrier wave signals to encode digital information for transmission and demodulates signals to decode the transmitted information. The goal is to produce a signal that can be transmitted easily and decoded to reproduce the original digital data. Modems can be used with any means of transmitting analog signals, from light emitting diodes to radio. A common type of modem is one that turns the digital data of a computer into modulated electrical signal for transmission over telephone lines and demodulated by another modem at the receiver side to recover the digital data.

A router connects multiple networks and routes network traffic between them.
It’s really that simple. In the case of your home network, your router has one connection to the Internet and one connection to your private local network. In addition, most routers also contain built-in switches that let you connect multiple wired devices. Many also contain wireless radios that let you connect Wi-Fi devices.
A modem serves as a bridge between the local network and the Internet.
Historically, the term “modem” is shorthand for modulator-demodulator. Modems were used to modulate the signals on telephone lines so that digital information could be encoded and transmitted over them and then demodulated—and decoded—on the other end. Though more modern broadband connections—like cable and satellite—don’t really work the same way, we kept using the term “modem” because it’s a device people were already familiar with and associated with connecting to the Internet.
The Advantages and Disadvantages of using a WiFi modem
In order to provide convenient, ISPs always gives their customers WiFi modem. In other word, you can enjoy WiFi in the same day when your ISP installed your home broadband. However, if you want to install a wireless router, many ISPs wouldn’t provide these devices without fees. So, what are the advantages and disadvantages of using a WiFi modem?
Advantages
As said above, you can use Wifi at the same day when installed your home broadband. You can save money, without buying a wireless router separately. Furthermore, If you don’t have much knowledge of deploying your home network, when you have a WiFi modem, you needn’t to study how to connect the wireless router and the modem.

Disadvantages
A combined modem, read carefully, “combined”, that is, the main function of modem is connecting Internet, while providing WiFi isn’t the main function of the modem.
A modem provides limited WiFi connection of devices. If there are many devices at your home
need WiFi, the modem can’t hold so many.
A modem always is installed outside your rooms, such as at your home door. You will find the WiFi signal is very weak when you walk into your room.
The Gigabit fiber modem given by most ISPs only supports 2.4 G mode. Therefore, the installation of optical fiber with a speed of more than 100 megabytes will affect the download speed of the devices to connect to the wireless network. Assuming that it is a 100M optical fiber, then the download speed will not exceed 10M per second through the 2.4 G mode connection.
Besides, the ISPs sometimes will not help you solve the problems of your wireless router. They only be responsible for their modem.

So, should I get a separate router?
The decision is ultimately up to you and depends on what you want. If you’re happy with your combined modem unit and you don’t want any additional features it doesn’t provide, you’ll probably just want to stick with the box your ISP gave you. It’s just easier to set up and use.
On the other hand, if you want the latest wireless hardware or additional features, you can get them by purchasing your own router and connecting it to your modem. You’re trading some simplicity for more power and choice.
Tips: How to connect the wireless router to the modem.
Hardware connection:
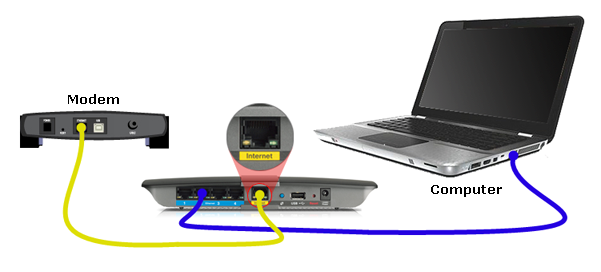
(1) Connect one end of the coaxial cable to the cable wall outlet, then connect the other end to the modem.
(2) Connect the modem power cord into an electrical outlet, then connect the other end to the modem.
Note: Most modems are always on and don’t have a power switch. If there is a power switch on the modem, turn it on.
(3) Connect one end of one Ethernet cable into the back of the modem, then connect the other end into the Wide Area Network (WAN) port on the router.
(4) Connect the router power cord into an electrical outlet, then connect the other end to the router.
(5) Connect the second Ethernet cable into port 1 on the router, then connect the other end into the back of the computer.
(6) Check the modem and router lights to confirm they have power, and connect to the network and your computer.
 Setting:
Setting:
(1) Open the browser, enter the setting URL of the router in the address bar, open the management interface of the router, enter the account number and password to log in.
What is the router setting URL? Check the router setting address through the sticker on the back of the router. Generally, the login address of each brand of router is usually marked on the sticker on the back of the router, which records the address, password, and serial number of the router’s management page.
(2) Click the function menu, select “Dynamic IP”, and click Next;
(3) Set the SSID and wireless password and click Next;
(4) Click “Finish” and the router will automatically restart.
(5) After the restart is complete, log in to the router management again, click Network Parameters> LAN Port Settings> enter the new IP address and save.
Recommend Routers
If you want to buy a useful wireless router, you can choose 5G routers, such as Huawei 5G CPE Pro, ZTE 5G MC801, Xiaomi Mi AX3600 Wifi 6 5G Router, etc.
Or choose WiFi 6 routers, including Huawei Wifi AX3 (Dual-Core) Wifi 6 Router, etc.

Related topics:
5G WiFi router: Huawei 5G CPE Pro vs. ZTE MC801
Huawei routing AX3 series released, Wi-Fi 6+ experience even better


