
Software-defined wide area network (SD-WAN) is gaining momentum, most of the enterprise’s technology can adapt to SD-WAN optimization, and the way providers provide services is constantly changing. There is also a trend in the industry to create a software-defined branch (SD-Branch) by managing many of the network functions of branch offices.
Today, we will introduce the features of SD-Branch.
-
What is SD-Branch?
SD-Branch is defined as a centralized management platform with SD-WAN, routing, network security and LAN/Wi-Fi functional integration. Software-based networking technologies, such as software-defined networking (SDN), software-defined WAN (SD-WAN), and network function virtualization (NFV), abstract network intelligence from integrated network devices (also known as black boxes).
The goal of SD-Branch is to use Network Virtualization to run multiple independent functions on a single platform. Chip technology from Intel, ARM and Broadcom enables networks to run routing, SD-WAN, network security and Wi-Fi functions on a single hardware platform.

-
SD-Branch Benefits
The most compelling advantage of SD-Branch is the increased operational agility, and IT organizations can quickly deploy and configure integrated branch office network solutions. They provide control and adjustment of all branch network and security features through a centralized management console.
In addition, SD-Branch is expected to reduce hardware costs by deploying software on consolidated hardware compared to many standalone devices.
Other SD-Branch advantages include:
- The cost of support and maintenance contracts is reduced because there are fewer vendors involved.
- With software virtualization, hardware requirements can be properly adjusted for each branch.
- Smaller hardware footprint makes it ideal for space-constrained branch offices.
- Network performance is scalable. As network requirements change, the performance of any feature can be adjusted by changing processor allocation or adding hardware resources.
- Because an energy-efficient platform replaces many devices, power consumption is lower.
Over time, SD-Branch will be easier to deploy, easier to manage, and more responsive to the changing needs of branch offices. As technology matures, the cost-effectiveness of CAPEX and OPEX can be significant.
-
SD-Branch Application Scenario
The best analogy for SD-Branch is single-function network devices (such as WAN optimization), and some SD-Branch solutions are better than others in some features.
The SD-Branch solution was initially suitable for newly deployed sites, mobile sites and small offices. Streamlined IT departments can benefit from the deployment and management capabilities of SD-Branch technology.
SD-Branch’s best use cases include:
- New branch or temporary branch, deployment speed and ease of use are critical Mobile office, such as public safety
- Major branch office updates, upgrades to a range of network devices
- Streamline branch offices, low data usage, most processing is done at the end SD-branch supplier
Due to the distributed functions in the current enterprise network, most branches have large numbers of specialized units, and SD-branch migration is a difficult task.
-
How many Companies provide SD-Branch?
Independent SD-WAN vendors like VeloCloud, Versa Networks, CloudGenix, 128 Technology and Cradlepoint.
Router vendors, including Cisco, Juniper, Nokia, and Huawei.
Ethernet switch vendors such as Cisco, Hewlett Packard Enterprise and Juniper Networks.
Wi-Fi experts, including HPE acquired by Aruba, Aerohive network, etc.
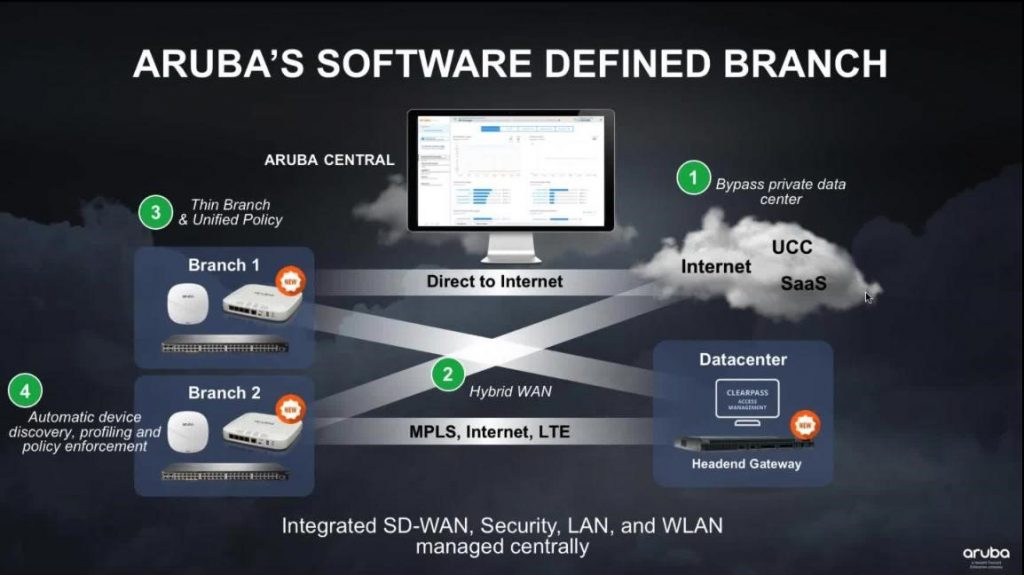
(Image from Aruba Company)
Products that add SD-WAN capabilities to WAN optimization vendors such as Riverbed, Citrix, Silver Peak and Talari.
Network security vendors, including Check Point Software, Palo Alto Networks and Zscaler.
-
4 things of SD-Branch we must know
Brad Casemore, vice president of data center network research at IDC, highlighted four things that IT infrastructure professionals need to know about SD-Branch.
(1). SD-Branch is the successor of SD-WAN
SD-Branch evolved from a software-defined WAN. SD-Branch can be seen in the same template as SD-WAN, it is a completely policy-based, automated branch office IT infrastructure approach, so its programmability makes it more flexible.
Essentially, the SD-Branch solution uses the same technology as SD-WAN, transforming the enterprise network and adding more features to make it suitable for branch offices.
(2). SD-Branch is more comprehensive than SD-WAN
The new SD-Branch solution includes more features. SD-WAN only handles connection problems to and from branch offices, and SD-Branch is more comprehensive than it. This centralized, orchestrated model can virtualize and chain all the functions of a branch.
For example, the SD-Branch solution provides other networking features such as LAN connectivity, security, and more that are not included in most SD-WAN solutions.
(3). SD-Branch saves costs
For companies, one of SD-Branch’s greatest attractions is the ability to save capital and operating expenses. Most branch offices use large numbers of “middle boxes” – dedicated devices for a variety of network and security purposes. The SD-Branch solution integrates all of these technologies, reducing the organization’s administrative costs because they only need to purchase one hardware without multiple.

In addition, the programmability and centralized management of SD-Branch products eliminates the need for IT staff at the branch office. This centralized approach to SD-Branch helps mitigate (if not eliminate) the overhead of IT branches, which reduces operational costs.
Eliminating IT branches can be a bad omen for network professionals because they may lose their jobs, but Casemore points out that most of the company’s branch offices have very few IT staff. This new technology can affect IT professionals, just as changing technology always affects them: they need to adapt their skills and adapt to new ways of working. But for those who have a deep understanding of the network, there will still be new roles given to them.
(4). Organizations should be cautious when choosing SD-Branch technology
When purchasing SD-Branch products, the company needs to conduct extensive investigations. SD-Branch needs to integrate with many other technologies, and companies need to make sure that the specific solution they choose will meet their needs.
You may also be interested in these Topics:
The Differences of IaaS, PaaS and SaaS
One Article to Understand the Cloud Computing, Virtualization, and Containers
Featured Cisco Products Help You Start with the Right Network



