
Having fast, reliable, and secure Internet is essential to operational success today. Do you know which connection option like fiber optic cable and copper Ethernet cable fits your company’s needs best? Ethernet cable or fiber optic cable?
In this article we will share the differences between the Ethernet cable and fiber optic cable, which help you decide which fits your company’s needs best: Ethernet cable or fiber optic cable.
The Basics: Ethernet Cable vs. Optical Fiber Cable
Ethernet Cable
Ethernet is a popular method of networking computers in a local area networks (LANs) using copper cabling.
In the past, Ethernet had a reputation for being slower than fiber optic cable, but that has started to change. Ethernet speed was once limited to 10 megabits per second (Mbps). However, “Fast Ethernet” offers speeds of up to 100Mbps, and “Gigabit Ethernet” can provide speeds of up to 1000Mbps.
Due to our ever increasing demand for speed, gigabit Ethernet is emerging as the go-to Ethernet option. Its cables are comprised of multiple strands of copper wire that are twisted together, with four twisted wire pairs per cable. Two of the pairs are used to send data, and the other two are used to receive data.
Data is transmitted via electrical signals sent through copper cabling. Cat 5e and Cat 6 cables are designed for high speed gigabit Ethernet.
Learn more: CAT-5, CAT-5e, CAT-6, and CAT-7-General Questions
Optical Fiber Cable
Today, optical fiber cables used for Internet are synonymous with speed, and are especially useful when transferring data over long distances.
The cable is made up of strands of incredibly thin optically pure glass that carry digital information with light instead of electrical currents used with Ethernet.
There are two basic types of fiber optic cable: single-mode and multi-mode.
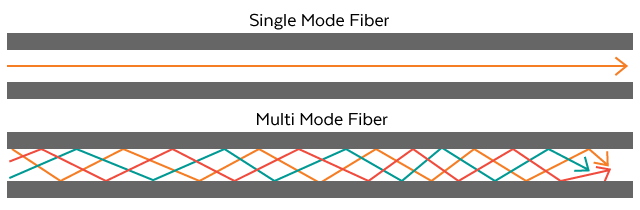
Single-mode fiber cables use laser light to send signals, and they are thinner than multi-mode fiber cables. Light-emitting diodes (LEDs) are used to send signals in multi-mode fiber cables, and multi-mode cables are usually used over short distances. Data transfer rates between 10 Mbps to 10 gigabytes per second (Gbps) are the norm.
Interference
Ethernet cables are vulnerable to electromagnetic interference because they work through electrical signals. However, using a “shielded” cable can help minimize this problem. A “shield” is a protective sheath that surrounds and protects the cable wires from electromagnetic leakage and interference. Although not always necessary, shielded cable is the preferred choice if you’re working close to strong electrical interference such as that produced by a generator?
Because optical fiber cables work through the transmission of light, interference from electronic devices isn’t a concern. Additionally, since they don’t conduct electricity, fiber optic cables are ideal for high voltage locations, in buildings prone to lightening strikes, and locations where explosive fumes are present.
Security
Due to the way in which data is transmitted across Ethernet copper cabling, it is vulnerable to being intercepted. Ethernet switches can help improve security.
Information sent via fiber optic cables is much more difficult to intercept because light can’t be read in the same way signals sent via copper cabling can be.
Speed
Until recently, fiber Internet-optic cable speed would almost always beat Ethernet cable speed. But as the technology behind Ethernet cables has advanced, Ethernet cables can provide speeds as fast as some fiber optic cables. As mentioned, gigabit Ethernet can provide data transfer speeds of up to 1000Mbps, but through the use of Cat 6 cables it can support data transfer rates of up to 10Gbps.
Typically, optical fiber transmits data faster than copper Ethernet cable and has the potential to be incredibly fast. In fact, a single optical fiber strand has been shown to transmit data at a rate of 100 terabits per second.
Fire Threat
Although the voltage used by Ethernet cable is usually insufficient to cause a fire, there is always electricity present in Ethernet cables.
Unlike Ethernet cable, optical fiber cable is non-flammable because it does not use electricity.
Capacity and Bandwidth
Copper cabling strands are thicker than optical fiber strands, so less wires can be bundled in a 22 gauge copper cable than in a 22 gauge optical fiber cable. Additionally, Ethernet offers less bandwidth. For example, a Cat 6a cable can relay 600 MHz over 100 m, but a multi-mode optical fiber cable can relay 1000 MHz over the same distance.
…Info from https://www.business.org/services/internet/ethernet-vs-fiber-basics/
Tips: How to Choose Right Ethernet Cable for your needs?
Ethernet cables can be roughly divided into the following three types: Straight-through cable (straight wire), Crossover cable (crossover cable) and Reverse cable (reverse cable).
Between equipment and equipment, how do we choose the connection cable?
1. Direct connection: usually used for connection between different devices:
Such as: host computer ←→ switch/hub;
Routers ←→ switches, hubs, etc.
Special case: when the router is directly connected to the host, a crossover cable is required
2. Crossover cable: usually used for connection between the same equipment:
Such as: exchange ←→ exchange; host ←→ host;
Hub ←→ switch; router ←→ host, etc.
3. Reverse line: used to connect the host to the console serial communication port (console) of the router/switch/firewall. After connecting, open the HyperTerminal on the host computer, you can configure the router, switch, etc.
More Related
How Does Optical Fiber Transmit Signal?
Cisco CCNA Part: Types of Ethernet Cabling


