There are many different Ethernet cables, such as Category 3, Cat5, Cat5e, Cat6, Cat6a, and Category 7. They are thick, flexible, but not the same.
These Ethernet cables are commonly used to connect a modem to a router, and, likewise, to connect a router to a computer’s network interface card (NIC) in modern networks.
Anyone who has plugged their computer into a broadband Internet connection such as cable or DSL has used an Ethernet cable.
What’s the difference between an ethernet cable and an ethernet “crossover” cable? We talked the differences between Ethernet Crossover Cable & Ethernet LAN Cable before.
And are you clear about the technical and physical differences between these popular Ethernet cables? In this article we will take a look at the main technical and physical differences between these Ethernet cables.
Ethernet cables are grouped into sequentially numbered categories (e.g. CAT5) based on different specifications; sometimes the category is updated with further clarification or testing standards (e.g. CAT5e, CAT6a). These categories are how we can easily know what type of cable we need for a specific application. Manufacturers are required to adhere to the standards which make our lives easier.
CAT Technical differences
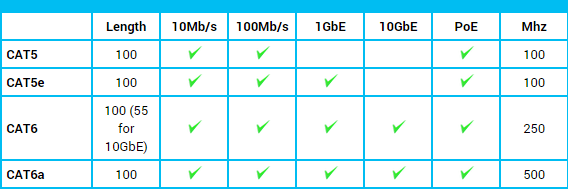
The difference in Ethernet cable specification is not as easy to see as physical changes, so let’s look at what each category does and does not support. Below is a chart for reference when picking cable for your application based on the standards for that category.
You may notice that as the category number gets higher, so does the speed and Mhz of the wire. This is not a coincidence, because each category brings more stringent testing for eliminating crosstalk (XT) and adding isolation between the wires.
Category 5 cable was revised in 2001, and mostly replaced with Category 5 Enhanced (CAT5e) cable which did not change anything physically in the cable, but instead applied more stringent testing standards for crosstalk. Category 6 was revised between 2002 with Category 6 Augmented (CAT6a) in 2008 that provided testing for 500 Mhz communication (compared to CAT6 250 Mhz). The higher communication frequency eliminated alien crosstalk (AXT) which allows for longer range at 10 Gb/s.
Physical Differences
So how does a physical cable eliminate interference and allow for faster speeds? It does it through wire twisting and isolation. Cable twisting was invented by Alexander Graham Bell in 1881 for use on telephone wires that were run alongside power lines. He discovered that by twisting the cable every 3-4 utility poles, it reduced the interference and increased the range. Twisted pair became the basis for all Ethernet cables to eliminate interference between internal wires (XT), and external wires (AXT).
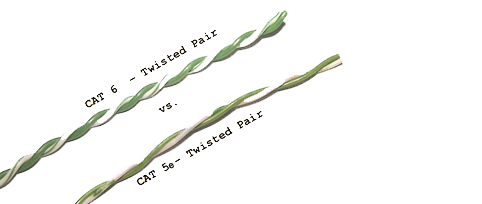
There are two main physical differences between CAT5 and CAT6 cables, the number of twists per cm in the wire, and sheath thickness.
Cable twisting length is not standardized but typically there are 1.5-2 twists per cm in CAT5 (e) and 2+ twists per cm in CAT6. Within a single cable, each colored pair will also have different twist lengths based on prime numbers so that no two twists ever align. The amount of twists per pair is usually unique for each cable manufacturer.
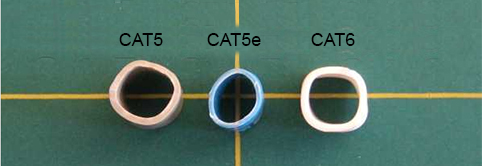
Many CAT6 cables also include a nylon spline which helps eliminate crosstalk. Although the spline is not required in CAT5 cable, some manufacturers include it anyway. In CAT6 cable, the spline is not required either as long as the cable tests according to the standard.
The nylon spline helps reduce crosstalk in the wire, with the thicker sheath protecting against Near End Crosstalk (NEXT) and Alien Crosstalk (AXT), which both occur more often as the frequency (Mhz) increases. In this picture below, the CAT5e sheath has the thinnest sheath versus CAT6 but it also was the only one with the nylon spline.
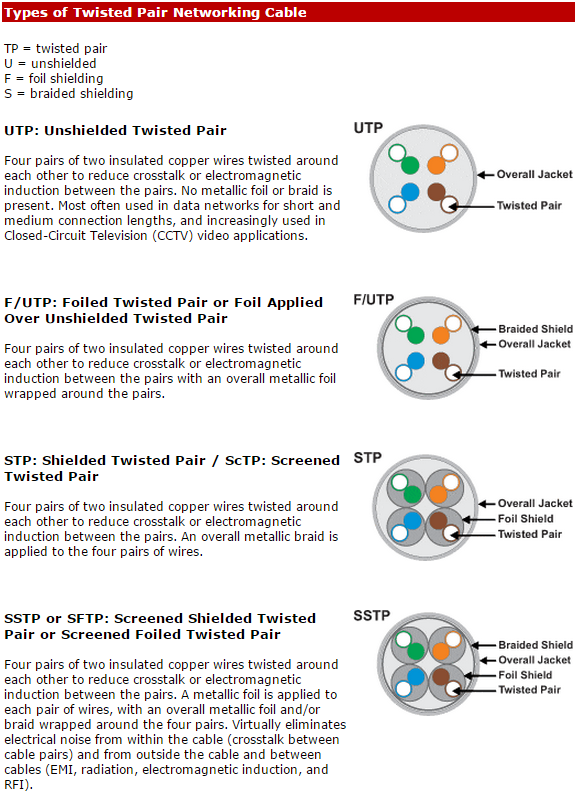
Shielded (FTP) vs. Unshielded (UTP)
Because all Ethernet cables are twisted, manufacturers use shielding to further protect the cable from interference. For example, Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) can easily be used for cables between your computer and the wall but you will want to use Foil Shielded Cable (FTP) for areas with high interference and running cables outdoors or inside walls.
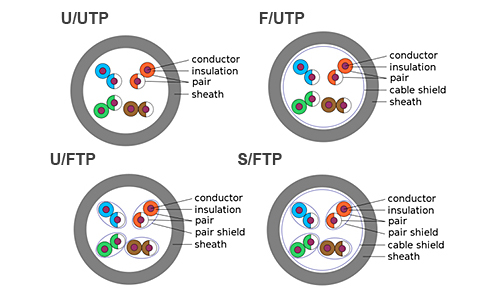
There are different ways to shield an Ethernet cable, but typically it involves putting a shield around each pair of wire in the cable. This protects the pairs from crosstalk internally. Manufacturers can further protect cables from alien crosstalk with additional cable shielding beneath the sheath. The diagram below shows the different types of Ethernet shielding and the codes used to differentiate them.
The code before the slash designates the shielding for the cable itself, while the code after the slash determines the shielding for the individual pairs: TP=twisted pair, U=unshielded, F=foil shielding, S=braided shielding
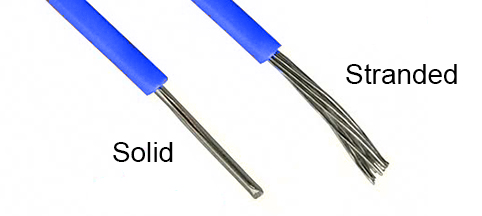
Solid vs. Stranded
Solid and stranded Ethernet cables refer to the actual copper conductor in the pairs. Solid cable uses a single piece of copper for the electrical conductor while stranded uses a series of copper cables twisted together. There are many different applications for each type of conductor, but there are two main applications for each type you should know about.
Key Differences
- Stranded cable is more flexible and should be used at your desk or anywhere you may be moving the cable around often.
- Solid cable is not as flexible but it is also more durable which makes it ideal for permanent installations as well as outdoor and in walls.
Reference Info from https://www.broadbandbuyer.co.uk/features/1917-what-the-difference-between-ethernet-cables/
More Related Ethernet Cable Topics
CAT-5, CAT-5e, CAT-6, and CAT-7-General Questions
Cisco CCNA Part: Types of Ethernet Cabling
Cisco Console Cables, Popular Types You Used
Ethernet Crossover Cable vs Ethernet LAN Cable