In the last previous article, we shared the Cisco Catalyst 4948E NetFlow-lite/NFLite in Detail, but do you know the deep relationship between NetFlow-Lite and nProbe, and how to use nProbe as NetFlow-Lite Collector? So in this article we will continue to talk about the NetFlow-Lite and nProbe. Firstly, let’s read some information about the NetFlow-Lite
What does NetFlow-Lite can do for you?
- The NetFlow-lite capability on Cisco Catalyst 4948E aims at providing traffic visibility into data center access layer, including server-to-server user-to-server activities.
- With the help of nProbe, netflow-lite can be analyzed and supported by any netflow collector that understand version5, 9 or IPFIX.
- Netflow-lite solution can be designed from a tiered approach for large scale data center: by deploying an nProbe per zone to summarize NetFlow-lite data within the zone, it reduces the amount of bandwidth overhead and allows data from multiple zones to be analyzed and gathered by a centralized netflow collector.
- nProbe & NetFlow-lite supports NetFlow version 9 and IPFIX.
- nProbe act as a collector to netflow-lite switches and as a probe to end collector. It works seamlessly with existing, already deployed NetFlow collector as well as allowing a wide choice of NetFlow collector for new deployment.
What is nProbe?
- NetFlow-Lite brings visibility to switched networks.
- NetFlow-Lite are exports in v9/IPFIX format and contain packets sections.
- Legacy NetFlow collectors need additional support to understand and analyze NetFlowlite flows.
NetFlow-Lite and nProbe
As stated above, nProbe is the first application to support NFLite. You might wonder what are the challenges behind this work. Some like these as follows:
- NFLite collector does not simply receive flows and dumps them on a DB (as most collectors do). It must also implement the flow cache that is a typical activity that a netflow probe does, and that is missing in collectors (they usually filter and aggregate flows, but nothing more than that).
- NFLite flows contain packet samples that are basically packets seen on switch ports, along with some metadata information such as the port on which such packet has been seen. This means that those packets need to be decoded (i.e. packet parsing) and consolidated into the flow cache. Dumping them on disk in raw format (as NetFlow collectors usually do) is useless as you can’t do much with them.
- Depending on the number of NFLite-aware switches, traffic and sampling rate, that send traffic towards the same nProbe, the amount of packets can be as high as 1-2 million flows/sec. Most NetFlow collectors can handle a sustained collection speed of a few tenth/hundred flows/sec, that is not adequate for providing accurate network visibility.
How to Use nProbe as NetFlow-Lite Probe/Collector?
In order to use nProbe with NFLite, you don’t have to do much.
Installation
- From Source
-
tar xvfz nProbe-xxx.tgz -
cd nProbe-xxx -
./autogen.sh -
make -
sudo make install
-
- From Binary Package
-
RedHat and Centos
-
rpm -i nprobe-xxx.rpm
-
Ubuntu/Debian
dpkg -i nprobe-xxx.deb
-
Windows
Use the graphical installer that comes with the nProbe package
Usage
As said before, with NFLite nProbe acts as both a collector (i.e. it collects and decodes NFLite flows received by NFLite devices such as Catalyst 4948E) and probe (towards a remote NetFlow collector).
Note that if your collector is nProbe itself, you can avoid sending converted flows to yet another nProbe instance, but you can use the same nProbe instance you used for NFLite conversion.
On the 4948E side you have to make sure the NFLite is properly configured. Example
netflow-lite exporter check
cos 0
dscp 60
ttl 254
transport udp 1000
template data timeout 60
options sampler-table timeout 60
options interface-table timeout 60
source 1.1.1.1
destination 1.1.1.3
export-protocol netflow-v9
!
netflow-lite sampler check
packet-rate 32
packet-section size 64
packet-offset 0
!
interface GigabitEthernet1/1
no switchport
ip address 40.40.40.1 255.255.255.0
netflow-lite monitor 1
sampler check
exporter check
A typical command line for starting nProbe is the following:
nprobe--collector-port 3000 -i none -n 5.5.5.10:2055 -b 2 -w 512000
Where:
- 3000 is the local UDP port on which NFLite flows are collected
- none means that nProbe does not capture packets from a physical device, but it rather receive flows via UDP. Note that you can start nProbe for both collecting NFLite flows and at the same time creating flows capturing packets from a specific interface.
- 5.5.5.5:2055 is the IP address and port of the NetFlow collector to which NFLite converted flows will be sent.
- 512000 is the initial size of the NetFlow cache that will be used for aggregating NFLite flows.
NetfFow-Lite is slated to come out on 4948E and 4948E-F in the next software release. As of today, NFLite support is part of nProbe for both Unix and Windows.
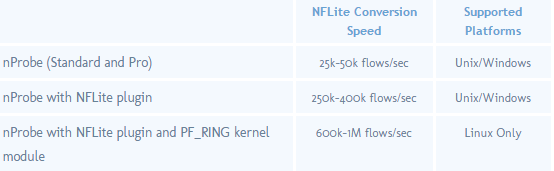
nProbe supports NFlite in three flavours:
More info https://www.ntop.org/products/nprobe/netflow-lite-plugin/
More Topics Related to Cisco NetFlow-Lite on the Cisco Catalyst 2960-X
Cisco NetFlow-Lite on the Cisco Catalyst 2960-X, 2960-XR, 2960-CX, and 3560-CX Series Switches