
Cisco unveiled a new member of the Integrated Services Router family at the end of June. The ISR 4451-X might not seem that unique at first glance. Here’s Cisco releasing another new router that adds to their already extensive branch router portfolio–the ISR G2. However, the newest ISR really is a ‘GameChanger’ when it comes to building a modern, future-proof network designed with business critical applications in mind.
That isn’t just marketing fluff in this case. The Cisco ISR 4451-X was designed from the ground up with rich network services and application delivery in mind. It really is the first platform conceived and built from the very beginning with a laser focus on application experience in a remote branch office. Maybe we even need a new name because in some ways it really is changing what it means to be a “router.”
Here we will have an overview on Cisco ISR 4451-X Router, which is prepared for future branch network needs. Is it your expectation? Let’s check it.
The Cisco ISR 4451-X Integrated Services Router is an attempt to create an entirely new concept in branch routing that ties together all of these trends into a platform that can seamlessly fit into branch environments at up to 2Gbps of throughput. The services include increased capacities for routing, switching, unified collaboration, security, WAN acceleration, application optimization and Application Visibility and Control (AVC). At the same time, the new routers are designed for expansion that can deliver increased performance and capabilities over time without the need for expensive system upgrades or hardware as remote sites grow.

The key new features and changes the Cisco 4451-X offers:
• Default forwarding bandwidth of 1 Gbps upgradable to 2 Gbps with a software-activated upgrade license
• The ability to house three network interface modules (NIMs) and two enhanced service modules (SM-Xs)
Comparison to the Cisco 3900 Series and Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation Services Routers
The Cisco 4451-X is positioned for high-end enterprise branch offices or enterprise headend where there is a performance requirement of 1 to 2 Gbps with services. Performancewise the Cisco 4451-X is positioned between the Cisco 3945E ISR and the Cisco ASR 1001.
Software of the Cisco 4451-X capable of running
The Cisco 4451-X Series runs the Cisco IOSXE Software. The initial version of software release will be the Cisco IOS XE Software Release 3.9.1 for the Cisco 4451-X. The Cisco 4451-X is similar to the Cisco ASR 1000 in terms of the software release that it runs on the system.
The Cisco ASR 1000 Shared Port Adapter (SPA) cards are not compatible with the Cisco 4451-X.
EHWIC modules available on the Cisco Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 (ISR G2) routers will not work with the Cisco 4451-X. The Cisco 4451-X is targeted at high-end branch-office environments, making most EHWICs unapplicable. Also, the newer NIM architecture allows for faster, more capable modules on a high-end platform.
The NIMs or service modules available on the Cisco 4451-X, but neither NIMs nor service modules will work with the Cisco ASR 1000 Series. NIMs are designed for a newer architecture and also will not work on the Cisco 1900, 2900, and 3900 Series Routers.
The Cisco UCS E-Series Modules are supported on the Cisco 4451-X.
We can use the Cisco Enhanced Service T3/E3 module (SM-X-1T3/E3) available on the Cisco 2900 and 3900 Series ISRs on the Cisco 4451-X. The Cisco Enhanced Service T3/E3 module SM-X-1T3/E3is supported on the Cisco 4451-X.
The Cisco 4451-X has separate data and control-plane memory. The control-plane memory comes as 4 GB default, upgradable to 16 GB. The data-plane memory comes as 2 GB default and is not upgradable today.
The Cisco 4451-X has three DIMM slots. Two slots are used for control-plane and one slot for data-plane memory.
In the case of control-plane memory, we cannot put a 4-GB DIMM in one slot and a 2-GB DIMM in the other slot. Like the Cisco 3900 Series, the Cisco 4451-X expects both the DIMM slots to have the same size of memory; that is, either 4-GB memory in both slots, making the control-plane memory size total 8 GB, or 2-GB memory in both slots, making the control-plane memory size total 4 GB. This setup is necessary because these platforms interleave memory devices for faster access.
All four ports with both RJ-45 and Small Form-Factor Pluggable (SFP) FPGE connections support failover. You can configure autofailover on any of the front-panel ports with both RJ-45 and SFP connections. When autofailover is configured, if the primary interface type fails, either RJ-45 or SFP, then the other media type becomes active and allows traffic to continue over the backup physical connection. In this scenario, the backup connection needs to be connected with the same speed and duplex as the primary connection.
Note that the autofailover feature as described does support one Gigabit Ethernet interface acting as a backup to another. The two physical connections available on a single Gigabit Ethernet interface simply provide failover if a link fails.
MDI crossover (MDI-X) is supported on the four onboard RJ-45 Ethernet interfaces.
The Cisco 4451-X uses the Multigigabit Fabric (MGF) for Layer 2 connectivity between the modules. The MGF can provide either 2 Gbps to all NIM slots or up to 10 Gbps to all SM-X slots. The MGF is completely nonblocking and can forward in excess of 50 Gbps.
All power-supply options for the Cisco 4451-X use a standard IEC C13 connector. No special IEC C15 cord is necessary for the Power over Ethernet (PoE) power supply, unlike the Cisco 3900 Series because higher-efficiency power supplies (85 percent) are used in the Cisco 4451-X. This cord thus helps lower the maximum current these power supplies can draw.
The Cisco 4451-X power supplies are hot-swappable. You do not need to power down the chassis to insert or remove a power supply. Also, unlike the Cisco 3900 Series, the bezel and fan tray can remain in place while a power supply is replaced.
There is no DC power-supply option for the Cisco 4451-X at first customer shipment (FCS). This enhancement is planned for future deployments.
The Cisco 4451-X has two PoE options. Two of the FPGE interfaces can be powered with the addition of a dedicated power-conversion module installed into the system (PWR-GE-POE-4400). This module does not require a higher-capacity system power supply and will work with the default 450W power supply. The PoE power for the FPGE ports is completely independent from PoE power to the rest of the system.
The Cisco 4451-X also has the option of a PoE power supply to provide PoE power to modules in the system such as an Ethernet switch module. This power supply actually includes two components as a single part: a higher-capacity 1000W system power supply and a PoE conversion module that converts system power into PoE for modules within the system. The Cisco 4451-X can accept up to two PoE power supplies and power-conversion modules for redundant operation or PoE Boost Mode.
The Difference between PoE Redundancy Mode and PoE Boost Mode
Both modes require that two power supplies be installed in the Cisco 4451-X. Redundancy mode provides 500W of PoE power to the chassis – the maximum amount a single power supply can offer – meaning that if a power supply fails the second power supply will be able to continue to deliver 500W of PoE power. PoE Boost Mode provides 1000W of PoE power – the maximum amount of power from both power supplies combined – meaning that if a single power supply fails the second redundant power supply will be able to provide only 500W of PoE power, cutting the amount of PoE power available by half.
There is no concept of primary or secondary power supply for the Cisco 4451-X. The power supplies are simply redundant and when one fails the other power-supply unit (PSU) takes over by transparently providing power to the entire system. No switching or intervention is required. Both share the load when running in the system; however, when one fails the other provides power to the complete unit. When the failed PSU is replaced with the new PSU in the system, the two power supplies are redundant.
PoE+ is available on the new SM-X Ethernet switch modules as well as on the FPGE ports.
The Cisco 4451-X uses both an inlet temperature and an altitude sensor to determine the best fan-speed setting. There are four different inlet temperature ranges and five different altitude ranges for a total of 20 possible different fan-speed settings. The addition of an altitude sensor is an industry first for a branch-office platform. With altitude data incorporated into the fan speed, the system can account for the density of air cooling in order to select the most efficient, and quietest, fan-speed setting. All system fans run at the same speed.
The Cisco 4451-X can handle the failure of a fan. A fully loaded system will function normally below 6000 feet (1.82 km) with a single fan failure. In the case where the Cisco 4451-X is above 6000 feet and in 32ºF (40ºC), it may shut down because of overheating. The system is rated to operate in 32Fº at up to 10,000 feet (3.05 km).
Failure of a power-supply fan will likely result in overheating and shutdown of the power supply. If power redundancy is required, you should install two power supplies.
The airflow information for the Cisco 4451-X follows:
• Maximum: 125 cfm
• Typical: 56 cfm
A rack-mount kit is available for the Cisco 4451-X. A rack-mount kit is part of the default accessory kit, and it is shipped with the Cisco 4451-X. Order part number ACS-4450-RM-19= for the spare 19-inch rack-mount kit for the Cisco 4451-X. By default the router will be shipped with this default 19-inch rack-mount kit.
The default accessory kit for Cisco 4451-X for Cisco 4451-X includes:
• Mechanical ground lug 90 feet per screw kit 19-inch rack-mount kit
• Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information (RCSI) roadmap document
• Plastic bag
• Shipping label
• Document pointer card for Cisco 4451-X
The GigabitEthernet0 is the dedicated management port on the Cisco 4451-X. This interface connects directly to the control-plane CPU and is ideal for managing the router through Telnet, Secure Shell (SSH) Protocol, Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP), and other management protocols. It is also ideal for downloading software images, uploading logs, and connecting to other management devices such as RADIUS, Network Time Protocol (NTP), Domain Name System (DNS), Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP), and TACACS servers. This interface should never be used for forwarding normal data traffic through the system because every packet goes directly to the control-plane CPU, bypassing the platform data plane. Because of this sensitivity, G0 is in a dedicated Mgmt-Intf Virtual Route Forwarding (VRF) port by default. This setup prevents accidental routing mistakes that could cause data traffic to be routed to the management network.
MDI-X is supported on the management RJ-45 Ethernet interface. The Cisco 4451-X has the option of the regular RJ-45 console port as well as the USB console port. As with the ISR G2 routers, only one console port can be used at a time, with preference given to the USB console port.
Online insertion and removal (OIR) is supported on the Cisco 4451-X. OIR is supported on the Cisco 4451-X for the following scenarios:
• Surprise insertion or removal of any NIM in any of the NIM slots
• Surprise insertion or removal of any SM-X in the SM-X slots
• Surprise insertion or removal of any power supply or system PoE conversion module
• Surprise replacement of the system fan tray; note, however, that this replacement must take place quickly enough that the system does not overheat, and depending on altitude and ambient temperature, the amount of time can vary greatly
Note that SM-X and NIM modules allow replacement only for like-to-like modules. A faulty module can be replaced with a good module of the same type but cannot be replaced with a completely different module of a different type.
To illustrate the Cisco 4451-X by MORE figures
Figure1: Bezel View of the Cisco ISR 4451-X
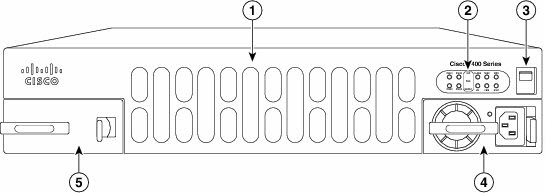
With one Power Supply Unit
| 1 | Router fan tray | 2 | LEDs |
| 3 | Router power On/Off switch | 4 | Power supply unit (PSU) |
| 5 | Optional power supply unit |
Figure2: Bezel side of
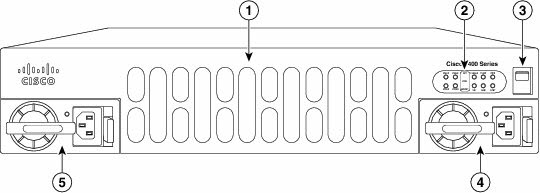
The Cisco ISR 4451-X with two PSUs
| 1 | Router fan tray | 2 | LEDs |
| 3 | Router power On/Off switch | 4 | AC power supply unit (P1) |
| 5 | AC power supply unit (P0) |
Figure3: Back Panel (I/O Side) Slots and Connectors on the Cisco ISR 4451-X
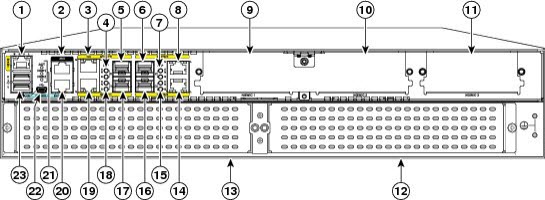
| 1 | GE 0 management port | 2 | Auxiliary port |
| 3 | RJ45 Gigabit Ethernet port (GE 0/0/0) | 4 | LEDs for the GE 0/0/0 interface |
| 5 | SFP Gigabit Ethernet port (GE 0/0/0) | 6 | SFP Gigabit Ethernet port (GE 0/0/2) |
| 7 | LEDs for the GE 0/0/2 interface | 8 | RJ45 Gigabit Ethernet port (GE 0/0/2) |
| 9 | NIM slot 1 | 10 | NIM slot 2 |
| 11 | NIM slot 3 (Optional Modular SSD Slot) | 12 | Enhanced Service Module (SM-X) 2 |
| 13 | Enhanced Service Module (SM-X) 1 | 14 | RJ45 Gigabit Ethernet port GE 0/0/3 |
| 15 | LEDs for the GE 0/0/3 interface | 16 | SFP Gigabit Ethernet GE 0/0/3 |
| 17 | SFP Gigabit Ethernet GE 0/0/1 | 18 | LEDs for the GE 0/0/1 interface |
| 19 | RJ45 Gigabit Ethernet port GE 0/0/1 | 20 | Serial Console Port |
| 21 | Console port USB 0 and USB 1 |
Figure4: Bezel Side LEDS of the Single PSU Cisco ISR 4451-X Model
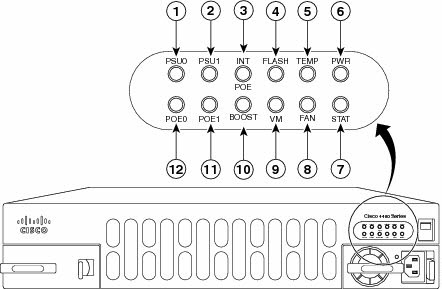
| 1 | PSU0: Power supply unit 1 | 2 | PSU1: Power supply unit 2 |
| 3 | INT POE: Internal PoE daughter card status | 4 | FLASH: Compact flash status |
| 5 | TEMP: Temperature status | 6 | PWR: Power |
| 7 | STAT: System status | 8 | FAN: Fan status |
| 9 | NGVM: Next generation voice module status | 10 | POE BOOST: Power over Ethernet boost mode |
| 11 | POE 1: Power over Ethernet 2 status | 12 | POE 0: Power over Ethernet 1 status |
Figure5: Ports and Slots on the Cisco ISR 4451-Xs
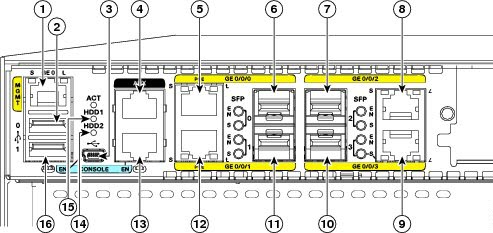
| 1 | Gigabit Ethernet management port | 2 | USB port 0 |
| 3 | USB console | 4 | Auxiliary port |
| 5 | Gigabit Ethernet port 0 | 6 | Small-form-factor pluggable (SFP) 0 |
| 7 | SFP 2 | 8 | Gigabit Ethernet port 2 |
| 9 | Gigabit Ethernet port 3 | 10 | SFP 3 |
| 11 | SFP 1 | 12 | Console port |
| 13 | Gigabit Ethernet port 1 | 14 | HDD 2 LED |
| 15 | HDD 1 LED | 16 | USB port 1 |
The NIMs and service modules will continue to function as they normally do after OIR on the Cisco 4451-X. Provided the OIR was carried out using a like-for-like module.
More Q and A to Know Cisco 4451-X well, you can see:
https://www.cisco.com/en/US/prod/collateral/routers/ps10906/ps12522/ps12626/qa_c67-728261.html
More Related Topics of Cisco 4451-X Integrated Services Router at Cisco.com
Cisco 4400 Series Integrated Services Routers-Data Sheets and Literature
https://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps12522/prod_literature.html
Hardware Installation Guide for the Cisco 4451-X Integrated Services Router
https://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/routers/access/4400/hardware/installation/guide/Overview.html
Cisco Integrated Services Routers Comparison—Cisco 4451-X, Cisco 3900, Cisco 2900 and Cisco 1900.
https://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps10536/prod_series_comparison.html
More Cisco Router Reviews and Tutorials:
Cisco Branch Routers, Accelerate Your WAN Performance
Cisco ISR-AX: Cheaper Branch Router with Bundled Layer 4-7 Services
Cisco Delivers “Monster” Catalyst Switch, Routers for SDN Environments


