When you configure a VLAN, you must assign it a number ID, and you can optionally give it a name. The purpose of VLAN implementations is to associate ports with particular VLANs. You configure the port to forward a frame to a specific VLAN.
Types of VLAN-you can configure a VLAN in voice mode to support voice and data traffic coming from a Cisco IP phone. You can configure a port to belong to a VLAN by assigning a membership mode that specifies the kind of traffic the port carries and the VLANs to which it can belong. A port can be configured to support these VLAN types:
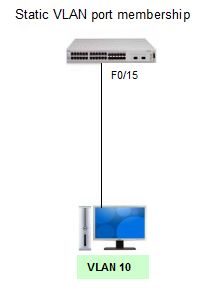
Static VLAN
This is when Ports on a switch are manually assigned to a VLAN. Static VLANs are configured using the Cisco CLI. This can also be accomplished with GUI management applications, such as the Cisco Network Assistant. However, a convenient feature of the CLI is that if you assign an interface to a VLAN that does not exist, the new VLAN is created for you.
Static Port mode configuration
Switch#config t
Switch(config)#interface fastEthernet0/15
Switch(config-if)#switchport mode access
Switch(config-if)#switchport access vlan 10
Switch(config-if)#end
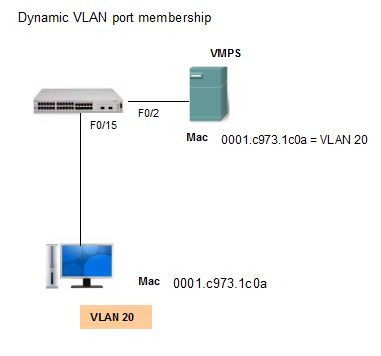
Dynamic VLAN
A dynamic port VLAN membership is configured using a special server called a VLAN Membership Policy Server (VMPS). With the VMPS, you assign switch ports to VLANs dynamically, based on the source MAC address of the device connected to the port. The benefit comes when you move a host from a port on one switch in the network to a port on another switch in the network; the switch dynamically assigns the new port to the proper VLAN for that host.
Voice VLAN
A port is configured to be in voice mode so that it can support an IP phone attached to it . Before you configure a voice VLAN on the port, you need to first configure a VLAN for voice and a VLAN for data.
Voice mode Configuration
Switch#config t
Switch(config)#interface fastEthernet 0/15
Switch(config-if)#mls qos trust cos
Switch(config-if)#switchport voice vlan 99
Switch(config-if)#switchport mode access
Switch(config-if)#switchport access vlan 10
Switch(config-if)#end
The configuration command mls qos trust cos ensures that voice traffic is identified and given priority traffic. Remember that the entire network must be set up to prioritize voice traffic. You cannot just configure the port with this command.
The switchport voice vlan 99 commands identifies VLAN 99 as the voice VLAN.
You can verify this by using the following command:
Switch1#show interfaces fa0/15 switchport
Name: Fa0/15
Switchport: Enabled
Administrative Mode: static access
Operational Mode: down
Administrative Trunking Encapsulation: dot1q
Negotiation of Trunking: off
Access mode VLAN: 10 (VLAN0010)
Trunking Native Mode VLAN: 1(default)
Administrative Native VLAN tagging: enabled
Voice VLAN: 99 (VLAN099)
The switchport access vlan 10 command configures VLAN 10 as the access mode (data) VLAN. You can see this verified in the bottom screen capture: Access Mode VLAN: 10 (VLAN0010).
—Reference from orbit-computer-solutions.com
More Related VLAN Tips:
‘What Happens in the VLAN Stays in the VLAN?’