
1.5G Frequency Bands
5th generation wireless systems, abbreviated 5G, are improved networks deploying in 2018 and later and may use existing 4G or newly specified 5G Frequency Bands to operate. The primary technologies include: Millimeter wave bands (26, 28, 38, and 60 GHz) are 5G and offer performance as high as 20 gigabits per second; Massive MIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output – 64-256 antennas) offers performance “up to ten times current 4G networks;” “Low-band 5G” and “Mid-band 5G” use frequencies from 600 MHz to 6 GHz, especially 3.5-4.2 GHz.
The 3GPP Release 15 of December, 2017 is the most common definition. Some prefer the more rigorous ITU IMT-2020 definition, which only includes the high-frequency bands for much higher speeds.
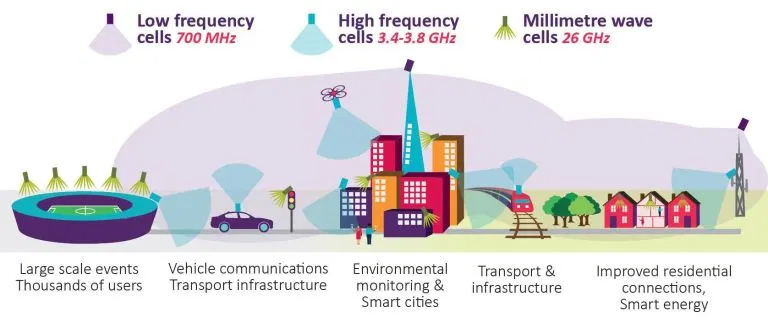
Figure 1. Expected 5G Frequency Band Usage: Reproduced courtesy OFCOM
 2.5G Frequency bands and channel bandwidths
2.5G Frequency bands and channel bandwidths
From 3GPP TS 38.101-1, the following table lists the specified frequency bands of 5G NR and the channel bandwidths each band supports. Superseded bands are indicated by a grey background.
Table 1. Frequency Range 1
| Band | Duplex mode | ƒ (MHz) | Common name | Subset of band | Uplink (MHz) | Downlink (MHz) | Duplex spacing (MHz) | Channel bandwidths (MHz) |
| n1 | FDD | 2100 | IMT | n65 | 1920– 1980 | 2110– 2170 | 190 | 5, 10, 15, 20 |
| n2 | FDD | 1900 | PCS | n25 | 1850– 1910 | 1930 – 1990 | 80 | 5, 10, 15, 20 |
| n3 | FDD | 1800 | DCS | 1710 – 1785 | 1805 – 1880 | 95 | 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30 | |
| n5 | FDD | 850 | CLR | 824 – 849 | 869 – 894 | 45 | 5, 10, 15, 20 | |
| n7 | FDD | 2600 | IMT-E | 2500 – 2570 | 2620 – 2690 | 120 | 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 40, 50 | |
| n8 | FDD | 900 | Extended GSM | 880 – 915 | 925 – 960 | 45 | 5, 10, 15, 20 | |
| n12 | FDD | 700 | Lower SMH | 699 – 716 | 729 – 746 | 30 | 5, 10, 15 | |
| n14 | FDD | 700 | Upper SMH | 788 – 798 | 758 – 768 | −30 | 5, 10 | |
| n18 | FDD | 850 | Lower 800 (Japan) | 815 – 830 | 860 – 875 | 45 | 5, 10, 15 | |
| n20 | FDD | 800 | Digital Dividend (EU) | 832 – 862 | 791 – 821 | −41 | 5, 10, 15, 20 | |
| n25 | FDD | 1900 | Extended PCS | 1850 – 1915 | 1930 – 1995 | 80 | 5, 10, 15, 20 | |
| n29 | SDL | 700 | Lower SMH | N/A | 717 – 728 | N/A | 5, 10 | |
| n30 | FDD | 2300 | WCS | 2305 – 2315 | 2350 – 2360 | 45 | 5, 10 | |
| n34 | TDD | 2100 | IMT | 2010 – 2025 | N/A | 5, 10, 15 | ||
| n38 | TDD | 2600 | IMT-E | 2570 – 2620 | N/A | 5, 10, 15, 20 | ||
| n39 | TDD | 1900 | DCS-IMT Gap | 1880 – 1920 | N/A | 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 40 | ||
| n40 | TDD | 2300 | S-Band | 2300 – 2400 | N/A | 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 40, 50, 60, 80 | ||
| n41 | TDD | 2500 | BRS | n90 | 2496 – 2690 | N/A | 10, 15, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 80, 90, 100 | |
| n48 | TDD | 3500 | CBRS (US) | 3550 – 3700 | N/A | 5, 10, 15, 20, 40, 50, 60, 80, 90, 100 | ||
| n50 | TDD | 1500 | L-Band | 1432 – 1517 | N/A | 5, 10, 15, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 80 | ||
| n51 | TDD | 1500 | L-Band Extension | 1427 – 1432 | N/A | 5 | ||
| n65 | FDD | 2100 | Extended IMT | 1920 – 2010 | 2110 – 2200 | 190 | 5, 10, 15, 20 | |
| n66 | FDD | 1700 | Extended AWS | 1710 – 1780 | 2110 – 2200 | 400 | 5, 10, 15, 20, 40 | |
| n70 | FDD | 2000 | AWS-4 | 1695 – 1710 | 1995 – 2020 | 300 | 5, 10, 15, 20, 25 | |
| n71 | FDD | 600 | Digital Dividend (US) | 663 – 698 | 617 – 652 | −46 | 5, 10, 15, 20 | |
| n74 | FDD | 1500 | Lower L-Band (Japan) | 1427 – 1470 | 1475 – 1518 | 48 | 5, 10, 15, 20 | |
| n75 | SDL | 1500 | L-Band | N/A | 1432 – 1517 | N/A | 5, 10, 15, 20 | |
| n76 | SDL | 1500 | Extended L-Band | N/A | 1427 – 1432 | N/A | 5 | |
| n77 | TDD | 3700 | C-Band | 3300 – 4200 | N/A | 10, 15, 20, 40, 50, 60, 80, 90, 100 | ||
| n78 | TDD | 3500 | C-Band | n77 | 3300 – 3800 | N/A | 10, 15, 20, 40, 50, 60, 80, 90, 100 | |
| n79 | TDD | 4700 | C-Band | 4400 – 5000 | N/A | 40, 50, 60, 80, 100 |
|
|
| n80 | SUL | 1800 | DCS | 1710 – 1785 | N/A | N/A | 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30 | |
| n81 | SUL | 900 | Extended GSM | 880 – 915 | N/A | N/A | 5, 10, 15, 20 | |
| n82 | SUL | 800 | Digital Dividend (EU) | 832 – 862 | N/A | N/A | 5, 10, 15, 20 | |
| n83 | SUL | 700 | APT | 703 – 748 | N/A | N/A | 5, 10, 15, 20 | |
| n84 | SUL | 2100 | IMT | 1920 – 1980 | N/A | N/A | 5, 10, 15, 20 | |
| n86 | SUL | 1700 | Extended AWS | 1710 – 1780 | N/A | N/A | 5, 10, 15, 20, 40 | |
| n89 | SUL | 850 | CLR | 824 – 849 | N/A | N/A | 5, 10, 15, 20 | |
| n90 | TDD | 2500 | BRS | 2496 – 2690 | N/A | 10, 15, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 80, 90, 100 |
Table 2. Frequency Range 2
| Band | ƒ (GHz) | Common name | Subset of band | Uplink / Downlink (GHz) | Channel bandwidths (MHz) |
| n257 | 28 | LMDS | 26.50 – 29.50 | 50, 100, 200, 400 | |
| 258 | 26 | K-band | 24.25 – 27.50 | 50, 100, 200, 400 | |
| n260 | 39 | Ka-band | 37.00 – 40.00 | 50, 100, 200, 400 | |
| n261 | 28 | Ka-band | n257 | 27.50 – 28.35 | 50, 100, 200, 400 |
3.Other Considerations for 5G Frequency Bands
These bands are usually available and can be quickly cleared for 5G use.
Table 3. High 5G Frequency Bands
| Geographical Area | 5G Frequency Band |
| Europe | 3400 – 3800 MHz (awarding trial licenses) |
| China | 3300 – 3600 MHz (ongoing trial) |
| China | 4400 – 4500 MHz |
| China | 4800 – 4990 MHz |
| Japan | 3600 – 4200 MHz |
| Japan | 4400 – 4900 MHz |
| Korea | 3400 – 3700 MHz |
| USA | 3100 – 3550 MHz |
| USA | 3700 – 4200 MHz |
4.Very High 5G Frequency Bands (MMW)
These bands will allow the deployment of hotspots providing very high throughput thanks to the large bandwidth available for operators:
Table 4. Very High 5G Frequency Bands (MMW)
| Geographical Area | 5G Frequency Band |
| Europe | 24.25 – 27.5 GHz for commercial deployments from 2020 |
| China | Focusing on 24.25 – 27.5 GHz and 37 – 43.5 GHz studies |
| Japan | 27.5 – 28.28 GHz trials planned from 2017 and potentially commercial deployments in 2020 |
| Korea | 26.5 – 29.5 GHz trials in 2018 and commercial deployments in 2019 |
| USA | 27.5 – 28.35 GHz and 37 – 40 GHz pre-commercial deployments in 2018 |
5.Lower 5G Frequency Bands (future considerations)
The bands 600 MHz, 700 MHz, 800 MHz, 900 MHz, 1.5 GHz, 2.1 GHz, 2.3 GHz and 2.6 GHz are considered for traditional coverage applications and new specific usages such as Internet of Things (IoT), Industry Automation, and Business Critical use cases. However “refarming” will be required for most of these bands, hence the time required to have them allocated to 5G will be much longer than the higher bands.
If you have different opinions on 5G Frequency Bands And Spectrum Allocations, please leave your comments.
Learn More:




