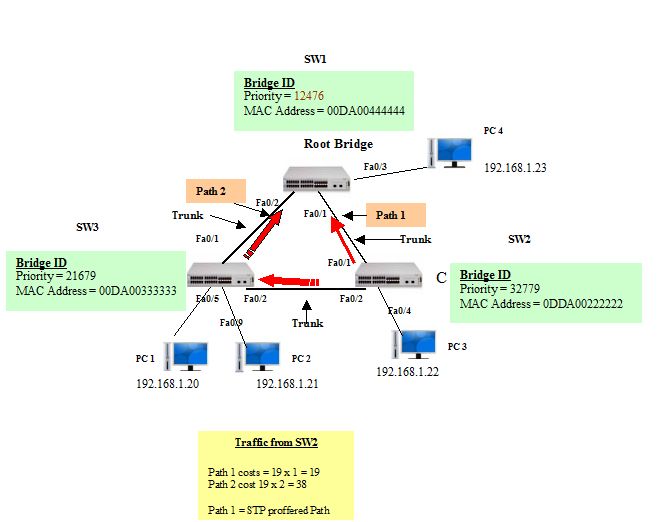
Best Paths to the Root Bridge
After the root bridge has been designated for the spanning tree process, the next process is to determine the best paths to the root bridge from all destinations in the network. The best path resolution is carried out by the summing up of the individual port costs along the path from the destination to the root bridge.
By default, port costs are defined by the speed at which the port operates. Every non-root bridge selects a root port; this is the port with the lowest cost path to the root bridge. Default costs depend on the speed of the link as set by IEEE (individual path cost = 19).
Note: costs may change as faster Ethernet is developed.
In the case of ports having the same cost; the use of port priority and port number can be applied. By default, Fa0/1 has 128.1 and Fa0/2 has 128.2
See table for finding the cost of a link:
| Link Speed | Revised Cost | Previous Cost |
| 10GBs | 2 | 1 |
| 1Gbs | 4 | 1 |
| 100Mbs | 19 | 10 |
| 10Mbs | 100 | 100 |
Configuring Port Costs
Although switch ports have a default port cost, it can be manipulated by configuration. Cisco switches provide the network administrator the ability to configure individual port costs. This enables an administrator full control of the spanning-tree paths to the root bridge.
To configure the port cost of an interface, enter the spanning-tree cost value command in interface configuration mode. Therange value can be between 1 and 200,000,000.
In the configuration example below, switch port F0/1 has been configured with a port cost of 30 using the spanning-tree cost 30 interface configuration command on the F0/1 interface.
SW2#config t
SW2(config)#interface fa0/1
SW2(config-if)#spanning-tree cost 30
SW2(config-if)#end
SW2#
To reset the port cost back to the default value, enter the no spanning-tree cost interface configuration command.
SW2#config t
SW2(config)#interface fa0/1
SW2(config-if)#no spanning-tree cost
SW2(config-if)#end
SW2#
You can use the show spanning tree command to very cost path.
So…
- Path cost is the sum of all the port costs along the path to the root bridge.
- The paths with the lowest path cost become the preferred path, and all other redundant paths are blocked.
- Every non-root bridge (switch) selects a root port
- The cost path from non-root bridge (switch) to the root bridge by default is 19 (IEEE)
- STP then configures the redundant path to be blocked, preventing a loop from occurring.
—Reference from orbit-computer-solutions.com
More Cisco & Networking Tips
How the Root Bridge and Ports are Chosen?
STP (Spanning Tree Protocol) Path Selection
How to Know What Device is on What Port on a Cisco Switch?
How to Configure Interfaces for the 3560 Switch?
How to Setup VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP) on Cisco Switches?