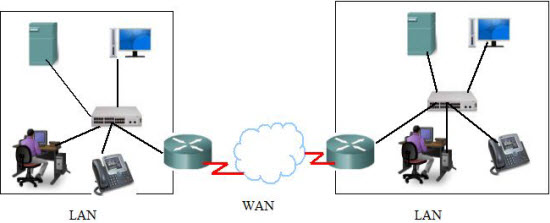
When an individual Company or Organization has locations that are separated by large geographical distances, it will be a matter of necessity to connect these individual locations so as to share, exchange and manager data or communication. To achieve this, the organization needs a Telecommunication Service Provider (TSP) to interconnect the LANs at the different locations.
Telecommunications Service Providers manage large area networks that can span long distances. TSPs transported voice and data communications on separate networks. These networks that connect LANs in geographically separated locations are referred to as Wide Area Networks (WANs).
WANs’ Main Function:
1. WANs generally connect devices that are separated by a broader geographical area than can be served by a LAN.
2. WANs use the services of carriers, such as telephone companies, cable companies, satellite systems, and network providers.
3. WANs use serial connections of various types to provide access to bandwidth over large geographic areas.
Main WAN Devices
There are specially designed network devices that are used to interconnect LANs. Configuring, installing and maintenance of this device requires expert skills by skilled technicians for the management of the organization’s network. These devices are specific to WAN environment, and they are: Modems, CSU/DSU, Access server, WAN Switch, Router, and Core Router
Modems enable digital data to be sent over an analogue medium during transmission and receiving of information. A voice band modem converts the digital signals produced by a computer – the 1s and 0s- into voice frequencies that can be transmitted over the analogue lines of the telephone network. On the other side of the connection, another modem converts the sounds back into a digital signal for input to a computer or network connection
CSU/DSU: Channel Service Unit / Data Service Unit CSU/DSU are combined piece of equipment used for monitoring clocking and frame synchronization on a line. It also performs error detection at the physical layer, It could be called a Modem sort of.
Access server: Concentrates dial-in and dial-out user communications. An access server may have a mixture of analogue and digital interfaces and support hundreds of simultaneous users.
WAN Switch: A multi-port internetworking device used in carrier networks. These devices typically switch traffic such as ATM, and operate at the Data Link layer of the OSI reference model. Public switched telephone network switches may also be used within the cloud for circuit-switched connections like Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) or analogue dialup.
Router: A Router Provides internetworking between the LANs, and WAN access interface ports that are used to connect to the service provider network. These interfaces may be serial connections or other WAN interfaces. With some types of WAN interfaces, an external device such as a DSU/CSU or modem (Analogue, Cable, or DSL) is required to connect the router to the local point of presence (POP) of the service provider.
Core Router: A router that resides within the middle or backbone of the WAN rather than at its periphery. To fulfil this role, a router must be able to support multiple telecommunications interfaces of the highest speed in use in the WAN core, and it must have the ability to forward IP packets at full speed on all of those interfaces. The router must also support the routing protocols being used in the core.