The Cisco Catalyst 4000/4500 switch family represents the entry-level chassis-based switch offering from Cisco. The Catalyst 4000/4500 switches are made up of three basic components:
- Chassis— This includes the switch chassis, power supplies, and fans.
- Supervisor engine— This includes the switch processor and switching engine and is required to operate the switch.
- Switching modules— These provide ports for connecting various types of devices to the switch.
Catalyst 4000/4500 Chassis
The chassis provided by the Catalyst 4000/4500 series switches vary across the Catalyst 4000 and Catalyst 4500 family. The major difference between the Catalyst 4000 series chassis and Catalyst 4500 series chassis is power; the Catalyst 4500 has an improved power distribution system that is capable of supporting inline power (i.e., the ability to power phones and wireless access points over Ethernet cabling) without requiring an external power shelf (as is required with the Catalyst 4000). The Catalyst 4500 series also provides a chassis that allows for redundant supervisor engines, whereas the Catalyst 4000 series chassis do not provide this.
Within the Catalyst 4000 series, two chassis are provided:
- Catalyst 4003— 3-slot chassis that provides one supervisor slot and two data slots.
- Catalyst 4006— 6-slot chassis that provides one supervisor slot and five data slots.
Within the Cisco Catalyst 4500 series, three chassis are provided:
- Catalyst 4503— 3-slot chassis that provides one supervisor slot and two data slots.
- Catalyst 4506— 6-slot chassis that provides one supervisor slot and five data slots.
- Catalyst 4507R— 7-slot chassis that provides two supervisor slots (one for redundancy) and five data slots.
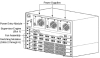
Figure 1-5 and Figure 1-6 shows examples of the Catalyst 4000 and 4500 chassis (the Catalyst 4006 and 4507R).
Figure 1-5 The Catalyst 4006 Chassis
Figure 1-6 The Catalyst 4507R Chassis
It is important to note that the Catalyst 2948G and Catalyst 2980G switches are essentially fixed configuration Catalyst 4000 switches with a Supervisor engine, power supply and a fixed configuration of 48 * 10/100BASE-T + 2 * 1000BASE-X ports (2948G) or 80 * 10/100BASE-T + 2 * 1000BASE-X ports (2980G). Figure 1-7 shows the Catalyst 2980G switch.
Figure 1-7 The Catalyst 2980G Switch
Supervisor Engines
The Catalyst 4000/4500 switch family consists of four Supervisor engines, which each vary in internal architecture, functionality, and operating system used for switch management. Table 1-6 describes each of the Catalyst 4000/4500 supervisors
Table 1-6—Cisco Catalyst 4000/4500 Supervisor Engines
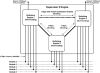
The Supervisor 1 and Supervisor 2 engines are Layer 2 switching only supervisors and are managed using the CatOS operating system. It is important to note that the Supervisor 2 contains a blocking architecture internally, meaning congestion is possible in certain configurations internally on the Supervisor. Figure 1-8 shows the internal blocking architecture of the Supervisor 2 switch.
Figure 1-8 Internal Architecture of Supervisor 2 Switch
NOTE
The Supervisor 1 is non-blocking, because it contains only a single 24-Gbps non-blocking switching engine that provides each of the 2-Gbps traces to module 2 and module 3 in the Catalyst 4003.
In Figure 1-8, notice that three separate switching engines (SEs) exist (each provide 24-Gbps internal non-blocking forwarding bandwidth), with each providing a 2-Gbps full-duplex trace to each module in the chassis (providing a total of 3 * 2-Gbps or 6-Gbps full-duplex bandwidth to each module).
Be careful of the “marketing terms” using by Cisco and other switch vendors to provide forwarding bandwidth performance figures. The quoted performance figures always refer to the total system bandwidth and not to the full-duplex bandwidth provided. For example, a 1-Gbps full-duplex connection is considered to provide a total of 2-Gbps bandwidth (1 Gbps in one direction, 1 Gbps in the other direction). In the case of SE1 and SE3 on a Catalyst 4000 Supervisor 2, each SE has 5 * 2-Gbps full-duplex connections to each line card, a single external 1-Gbps full-duplex 1000BASE-X connection on the supervisor and a 1-Gbps full-duplex connection to SE2. This provides a total of 12 Gbps full-duplex bandwidth (5 * 2 + 1 + 1), or a total forwarding bandwidth of 24 Gbps.
Although each SE is non-blocking internally, a single 1-Gbps full-duplex connection interconnects the switching engines, which potentially causes blocking (congestion) on the interconnections between each SE if devices attached to one switching engine are communicating with devices attached to another switching engine.
NOTE
If you are not using the two external 1000BASE-X ports on the Supervisor 2 module, you can disable them by configuring switch acceleration and introduce a third 1-Gbps interconnection between SE1 and SE3, reducing the amount of potential blocking (see dashed connection between SE1 and SE3 in Figure 1-8). You can also purchase a backplane channel module for the Supervisor 2, which doubles the bandwidth between each switching engine from 1 Gbps to 2 Gbps.
The Supervisor 3 and Supervisor 4 engines are Layer 2 and Layer 3 switching capable and are managed using the Cisco IOS operating system. These supervisors are completely non-blocking internally, unlike the Supervisor 1 and Supervisor 2, consisting essentially of one large non-blocking switching engine to which each module trace connects to. Just as for the Catalyst 3550/3750 switches, a basic image provides Layer 3 switching using static and RIP routing, whilst a separate enhanced image provides full Layer 3 switching using static, RIP, IGRP, EIGRP, OSPF, and BGP routing.
NOTE
The differences between the Supervisor 3 and Supervisor 4 include memory (128 MB in Supervisor 3, 256 MB in Supervisor 4); support for redundant supervisors (Supervisor 4); and the ability to add a NetFlow feature daughter card (Supervisor 4).
Switching Modules
The Catalyst 4000/4500 switch family provides for a wide variety of switching modules, allowing for high-density 10/100BASE-T, 10/100/1000BASE-T, and 1000BASE-X deployments. Other modules supported include a Layer 3 routing module (for Supervisor 1/2 deployment, not supported in Supervisor 3/4) and an access gateway module (provides voice gateway functionality). Table 1-7 lists some of the switching modules available for the Catalyst 4000/4500.
Table 1-7. Cisco Catalyst 4000/4500 Switching Modules
| Module Part Number | Description |
| WS-X4148-RJ | 48 x 10/100BASE-T RJ-45 ports |
| WS-X4148-RJ45V | 48 x inline powered 10/100BASE-T RJ-45 ports |
| WS-X4148-RJ21 | 48 x 10/100BASE-T ports with RJ-21 Telco connectors |
| WS-X4232-GB-RJ | 32 x 10/100BASE-T + 2 x 1000BASE-X |
| WS-X4232-L3 | Layer 3 Router module
32 x 10/100BASE-T and 2 x 1000BASE-X ports |
| WS-X4424-GB-RJ45 | 24 x 10/100/1000BASE-T |
| WS-X4448-GB-RJ45 | 48 x 10/100/1000BASE-T |
| WS-X4448-GB-LX | 48 x 1000BASE-LX |
| WS-X4306-GB | 6 x 1000BASE-X |
| WS-X4418-GB | 18 x 1000BASE-X |